What is supply chain supply chain sustainability? It describes a supply chain’s resilience and ability to support continuous business growth, from product compliance to product sustainability.
There are different approaches to sustainability. Operational sustainability focuses on issues like energy usage, working conditions, and other concerns within an organization’s four walls, while supply chain sustainability encompasses a manufacturer’s entire supply chain impact.
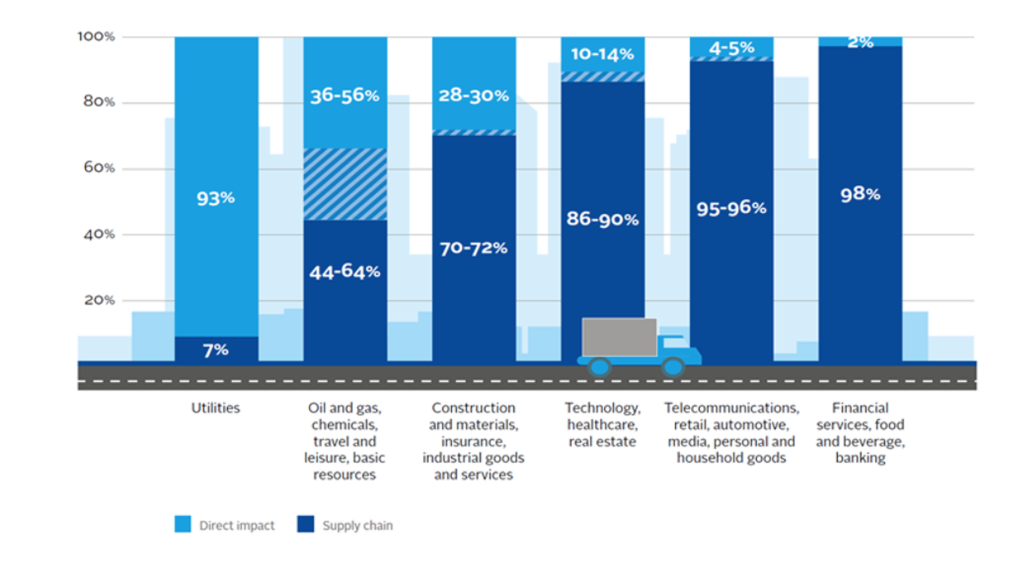
For many industries, the majority of a manufacturer’s footprint is found within the supply chain, not as a direct result of operations. According to a study by the Principles for Responsible Investment, more than 80–90% of a manufacturer’s environmental footprint, air emissions, and pollution occur in supplier activities and shipping.
The Three Pillars of Sustainable Supply Chains
When it comes to sustainability management and reporting, there are three main factors to consider: environmental, social, and governance. Together, they’re often known as supply chain ESG. If sustainability is the end goal, ESG is the roadmap.
Environmental
Covers how your supply chain relates to climate change, deforestation, pollution, waste management, packaging recyclability, and more.
| Impact | Supply Chain Consideration |
| Climate | GHG emissions, reduction targets, renewable energy |
| Resource Use | Water and wastewater management, waste and hazardous materials management |
| Biodiversity | Cotton, natural rubber, forestry |
| Product Stewardship | Hazardous chemicals, lifecycle management, packaging and end-of-life, safe handling/storage/disposal |
Social
Focuses on how supplier’s business practices affect both the global community and their own workforce. This includes safe working conditions, workplace diversity, fair compensation, forced or child labor, and conflict minerals.
| Impact | Supply Chain Consideration |
| Labor Rights | Child labor, occupational safety, wages/benefits/hours, discrimination/harassment, freedom of association |
| Human Rights | Security forces, data protection, land/property/housing rights |
| Diversity & Inclusion | Ownership classification, diversity certification, workforce demographics |
Governance
Addresses how an organization in your supply chain governs itself (such as a supplier code of conduct), enforces policies, discloses information, and meets stakeholder needs.
| Impact | Supply Chain Consideration |
| Organizational Commitment | Business ethics, bribery and corruption, conduct, antitrust, whistleblower protections |
| Resiliency | Business continuity and planning |
| Data Protection & Privacy | Data protection, privacy |
For each of these, you will need to engage your suppliers for data about their operations and goals. You will also need to educate them about how their actions affect your supply chain sustainability goals. Finally, you’ll want to track supplier sustainability scores across your supply chain so you can track progress and sustainability risks. The more you support your partners and help them overcome supplier fatigue, the faster you’ll reach your goals.
Diving Deeper into Supply Chain Sustainability
Because supply chain sustainability spans everything from environmental impacts to human rights and governance, it provides a more actionable lens to address external factors outside your direct control.
It focuses on seeing your operation’s entire footprint. Specifically, it means seeing deep into your supply chain to understand where materials come from, where they go before reaching your manufacturing sites, and who handles those materials along the way.
A supply chain sustainability framework provides reassurance and visibility. With it, manufacturers can be sure materials don’t contain conflict materials, utilize forced or child labor, or impact environmental sustainability.
Finally, with an effective supply chain sustainability solution, manufacturers can anticipate future supply chain redesigns or shortages to mitigate risk and positively affect the world around them.
How to Improve Supply Chain Sustainability Management With Assent
Assent’s supply chain sustainability platform — including ESG reporting software, extended producer responsibility solutions, and responsible sourcing reporting — allows you to:
- See your entire operational footprint
- Understand where materials originate, who handles them, and how they are processed
- Ensure materials do not contain conflict minerals, use forced or child labor, or harm environmental sustainability
- Anticipate future supply chain redesigns or shortages to mitigate risk
Attaining Supply Chain Sustainability
Because supply chains weren’t built with sustainability in mind, manufacturers need a strong foundation for their programs — one that goes beyond direct suppliers. Assent provides solutions specifically for manufacturers to build sustainability programs that enable smarter work and sustainable growth.
FAQ: Supply Chain Sustainability
Supply chain sustainability is becoming a critical focus for businesses that want to reduce risk, improve resilience, and grow responsibly. This FAQ answers common questions about sustainable supply chain management, key practices, and the role of software in building stronger, more transparent supply chains.